DSDNet: Raw Domain Demoiréing via Dual Color-Space Synergy
(ACMMM 2025)
Abstract
With the rapid advancement of mobile imaging, capturing screens using smartphones has become a prevalent practice in distance learning and conference recording.
However, moiré artifacts, caused by frequency aliasing between display screens and camera sensors, are further amplified by the image signal processing pipeline, leading to severe visual degradation.
Existing sRGB domain demoiréing methods struggle with irreversible information loss, while recent two-stage raw domain approaches suffer from information bottlenecks and inference inefficiency.
To address these limitations, we propose a single-stage raw domain demoiréing framework, Dual-Stream Demoiréing Network (DSDNet), which leverages the synergy of raw and YCbCr images to remove moiré while preserving luminance and color fidelity.
Specifically, to guide luminance correction and moiré removal, we design a raw-to-YCbCr mapping pipeline and introduce the Synergic Attention with Dynamic Modulation (SADM) module.
This module enriches the raw-to-sRGB conversion with cross-domain contextual features.
Furthermore, to better guide color fidelity, we develop a Luminance-Chrominance Adaptive Transformer (LCAT), which decouples luminance and chrominance representations.
Extensive experiments demonstrate that DSDNet outperforms state-of-the-art methods in both visual quality and quantitative evaluation and achieves an inference speed 2.4x faster than the second-best method, highlighting its practical advantages.
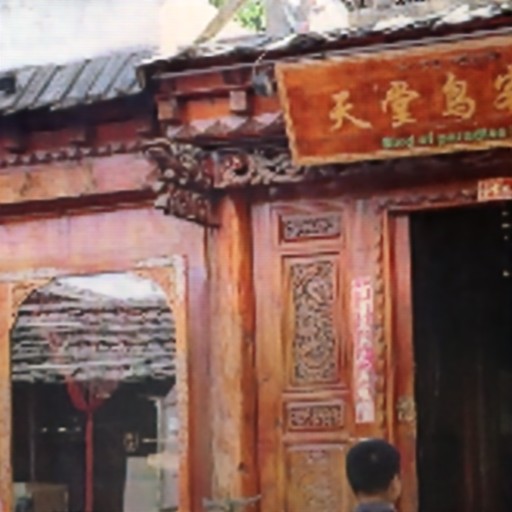
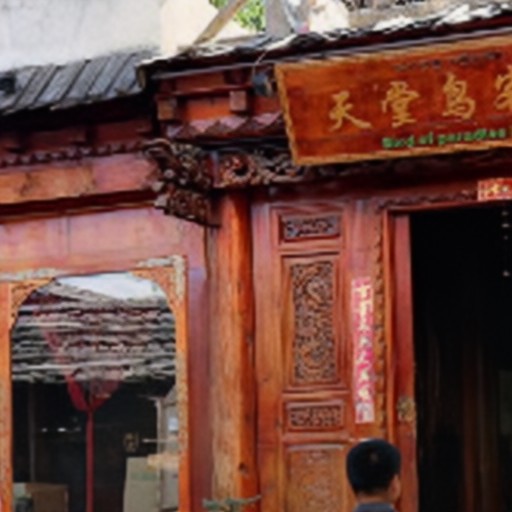
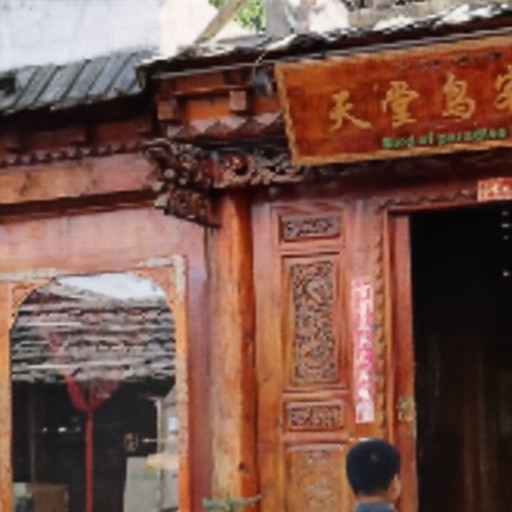
Comparison of DSDNet with other methods on TMM22 dataset
CR3Net
Ours
RRID



CR3Net
Ours
RRID
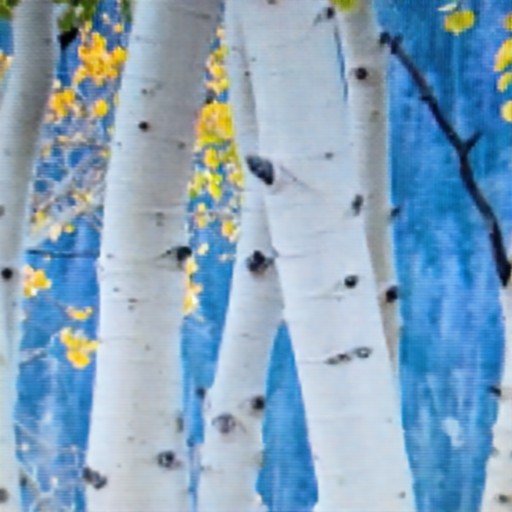
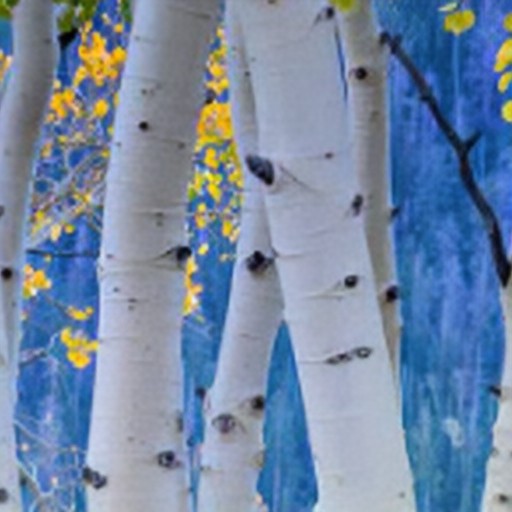
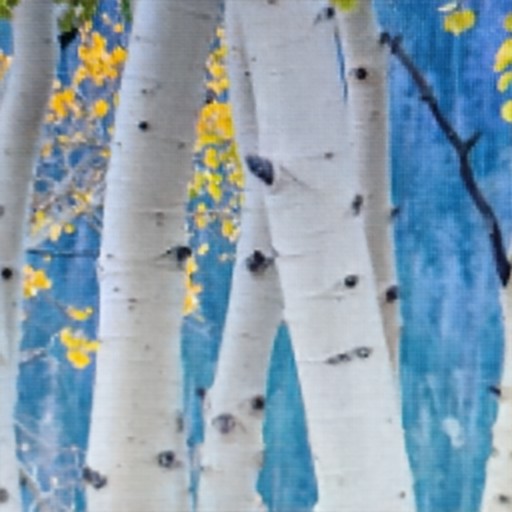



CR3Net
Ours
RRID
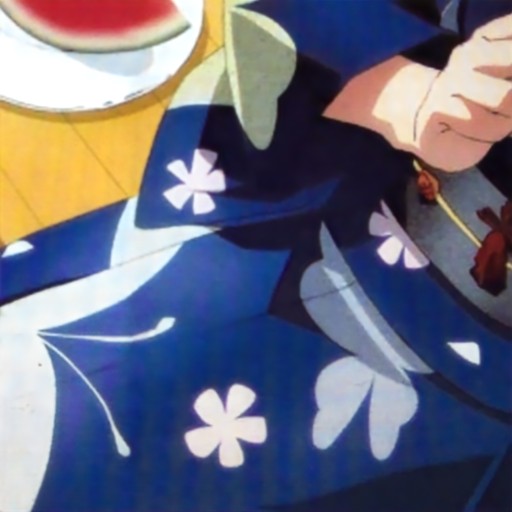
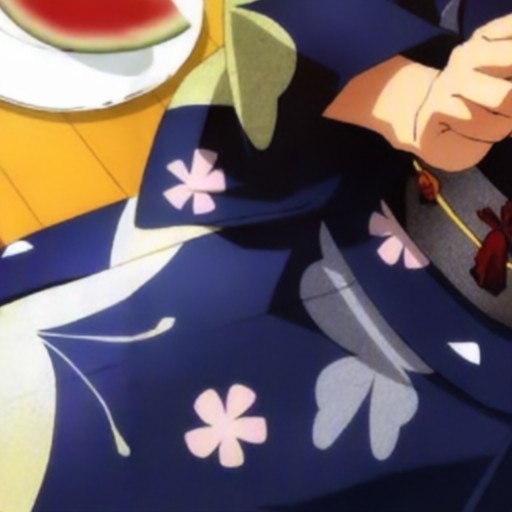
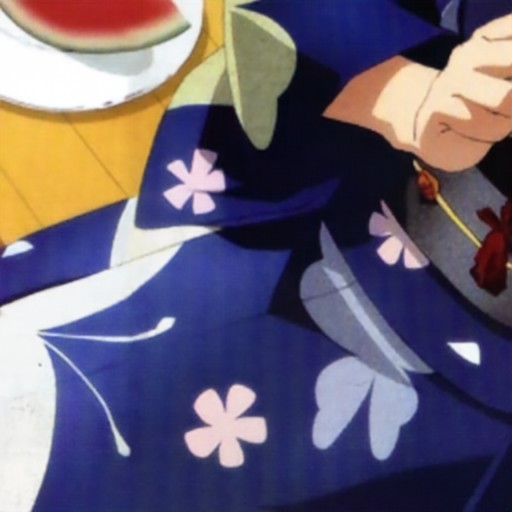



CR3Net
Ours
RRID
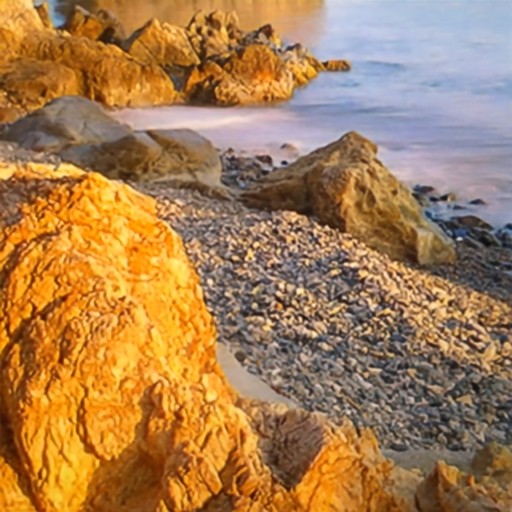
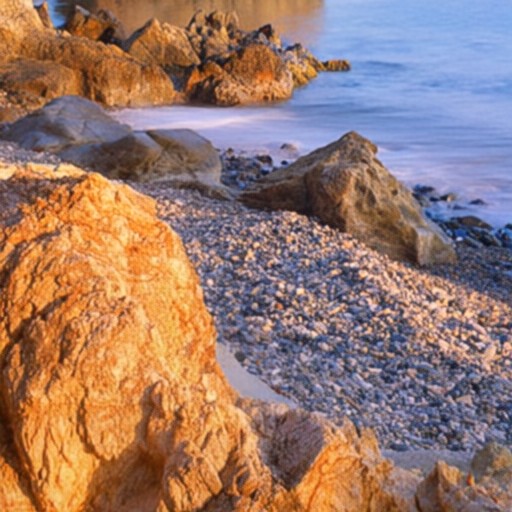
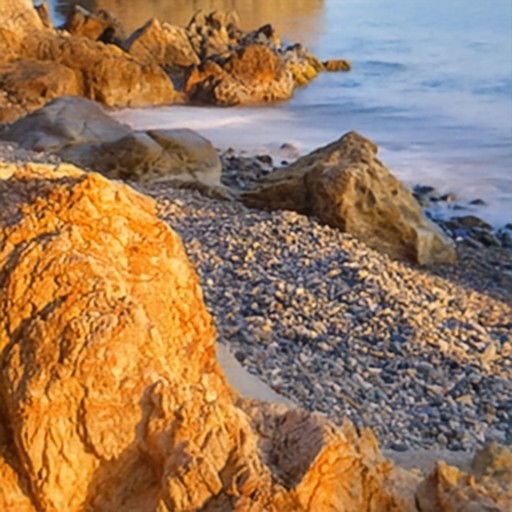



CR3Net
Ours
RRID

CR3Net
Ours
RRID
CR3Net
Ours
RRID
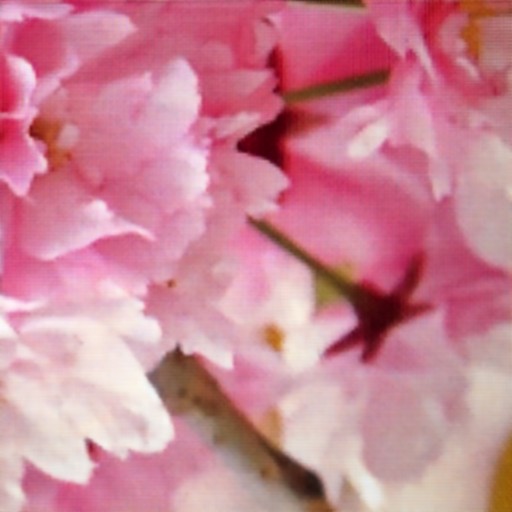
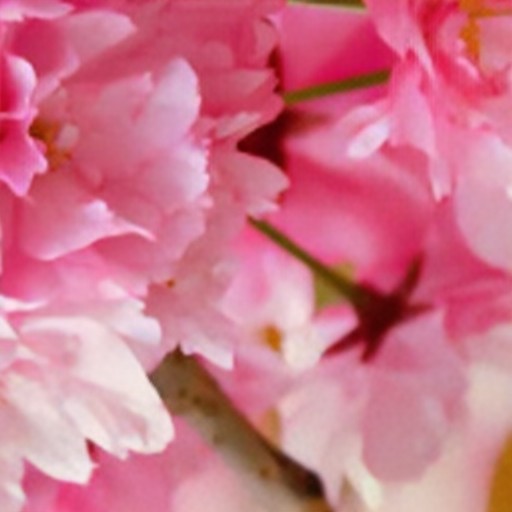
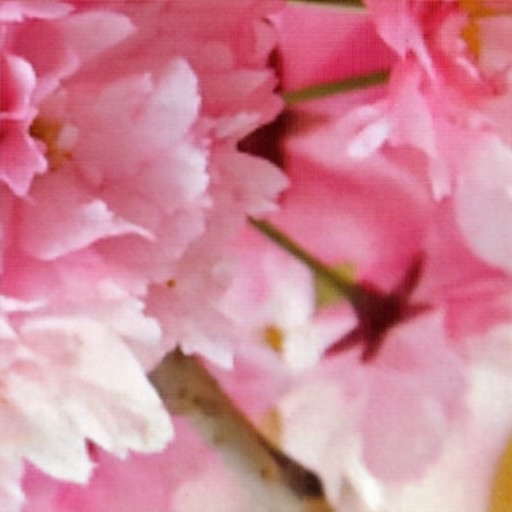



CR3Net
Ours
RRID
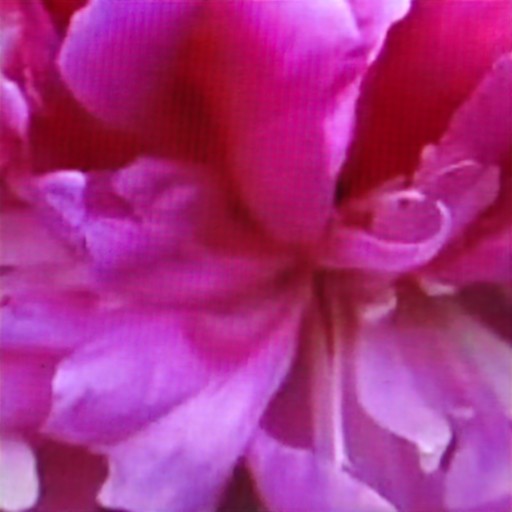
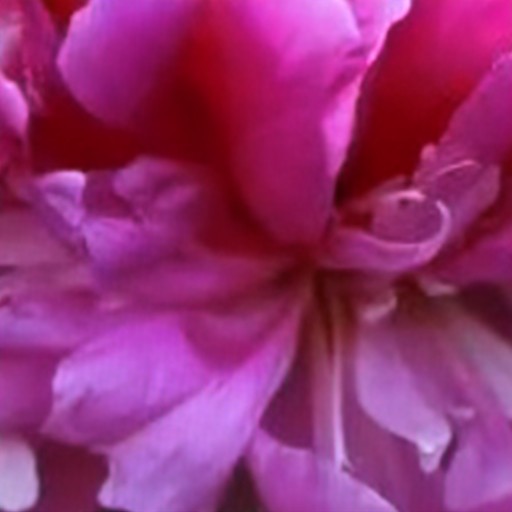
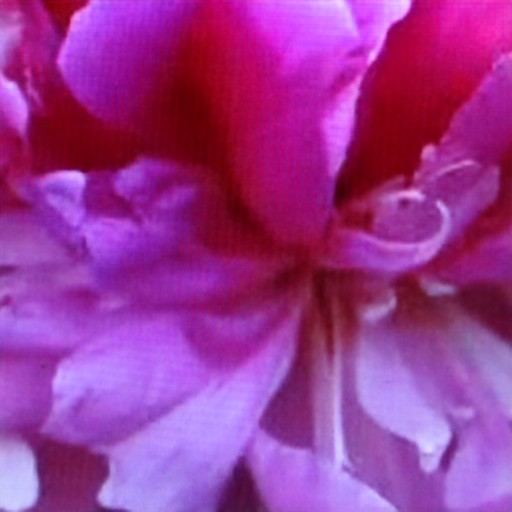



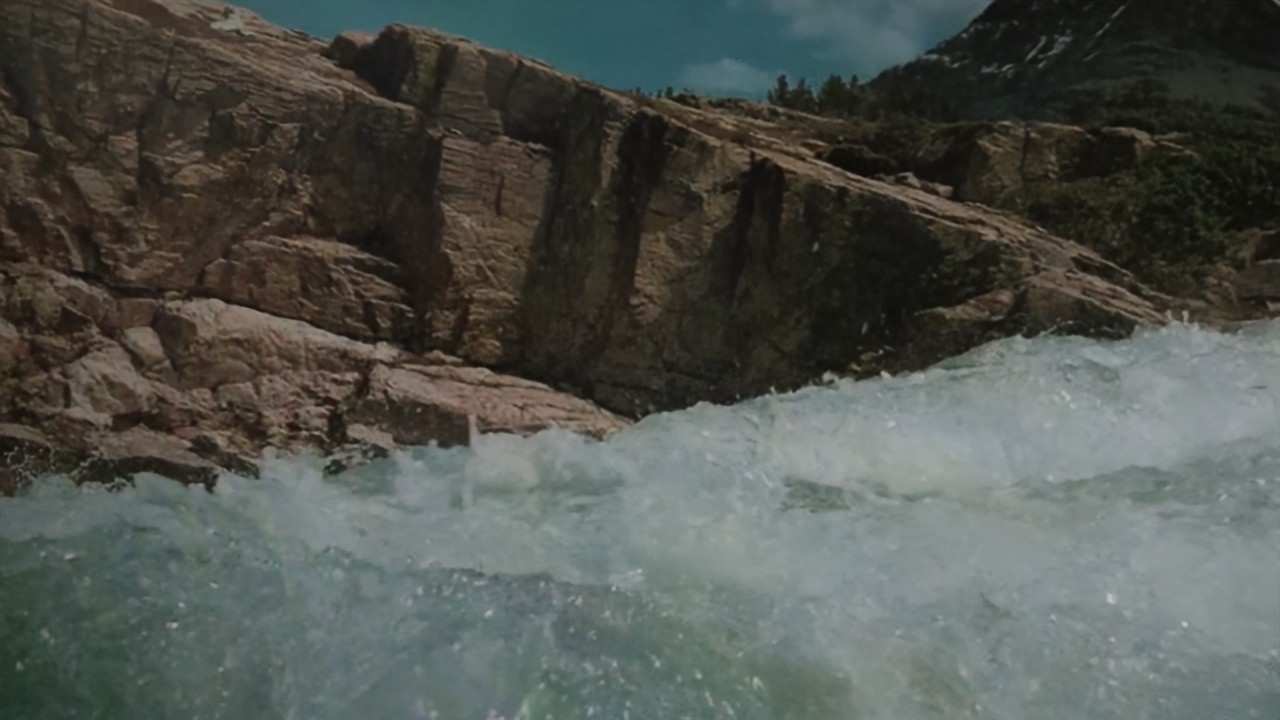
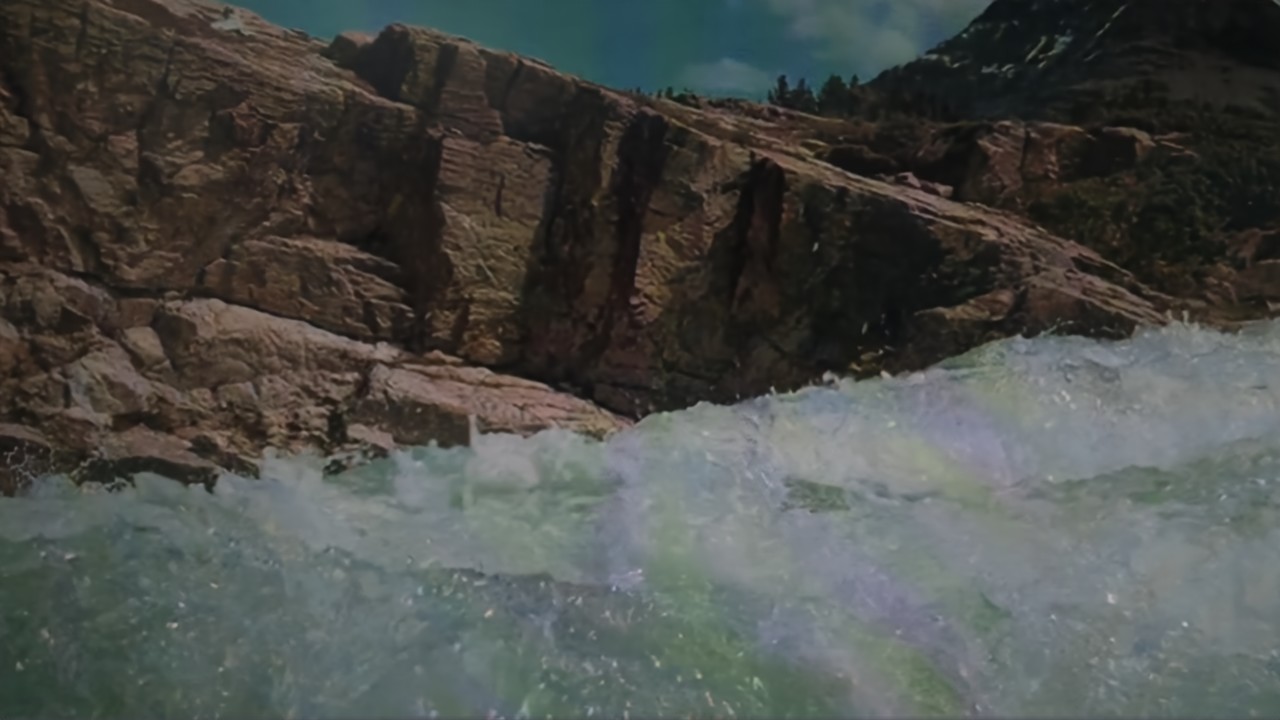
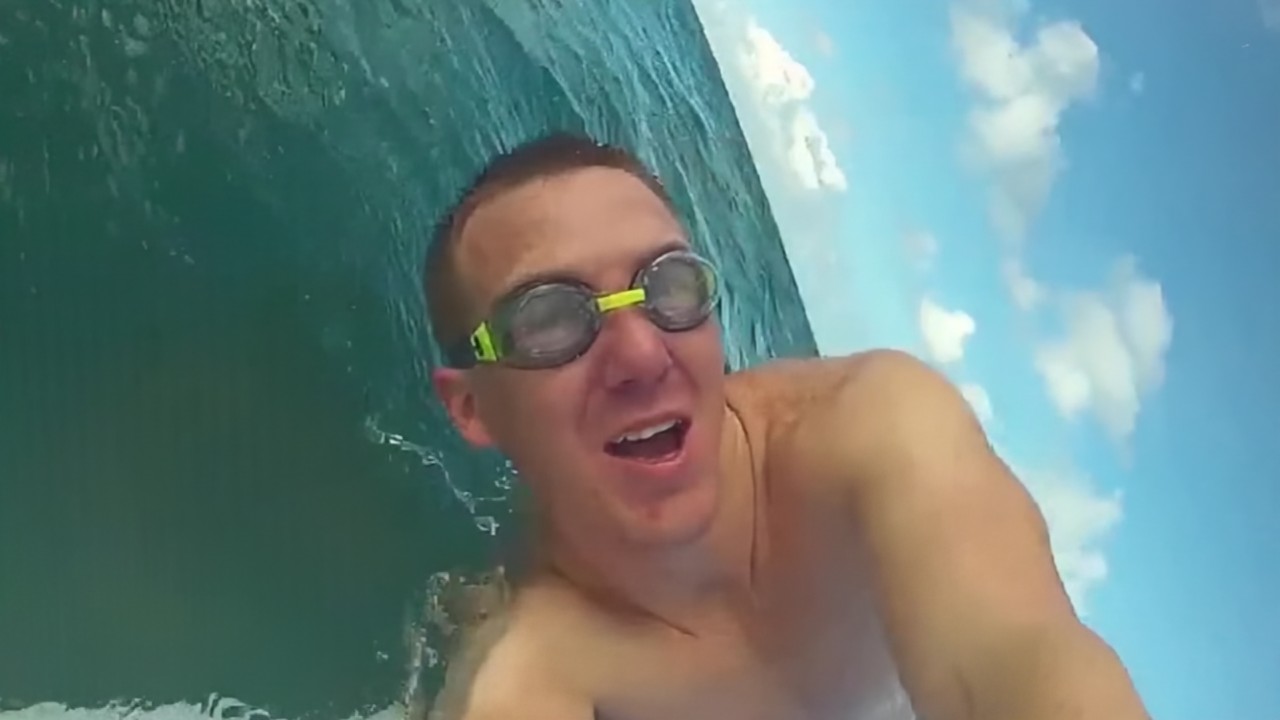
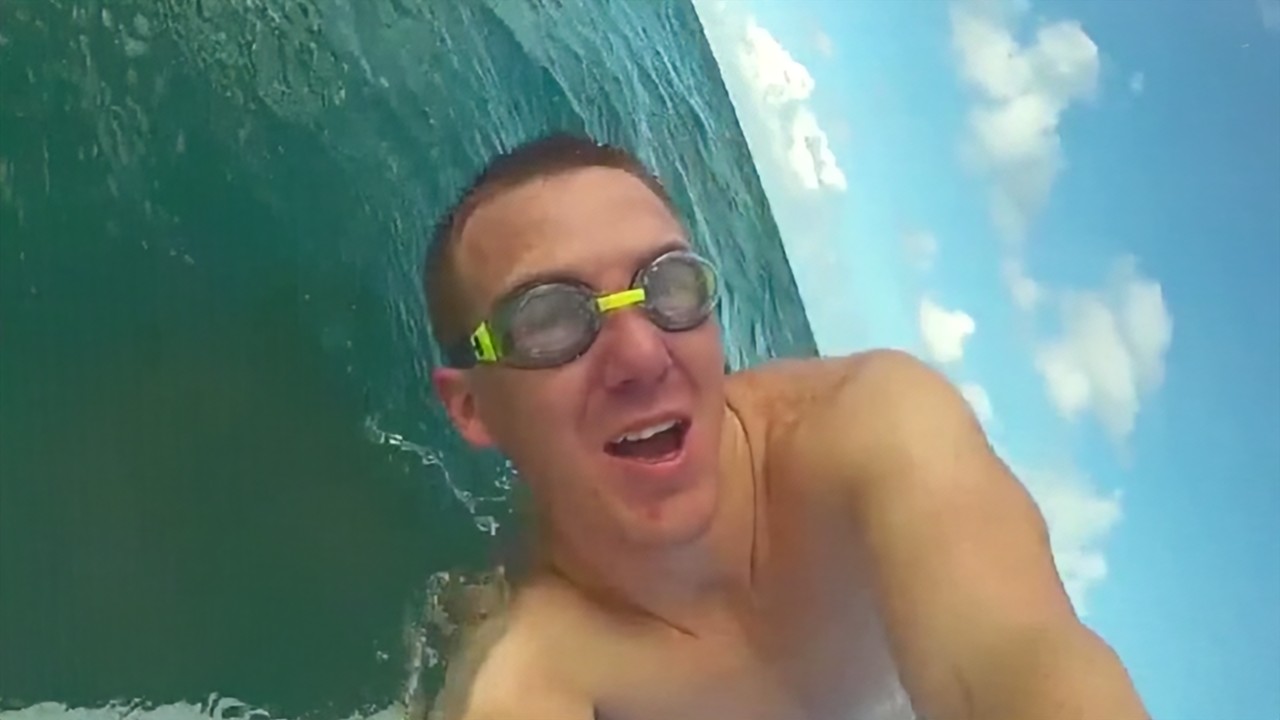
Comparison of DSDNet with other methods on RawVDemoiré dataset
RawVDemoire
Ours
RRID
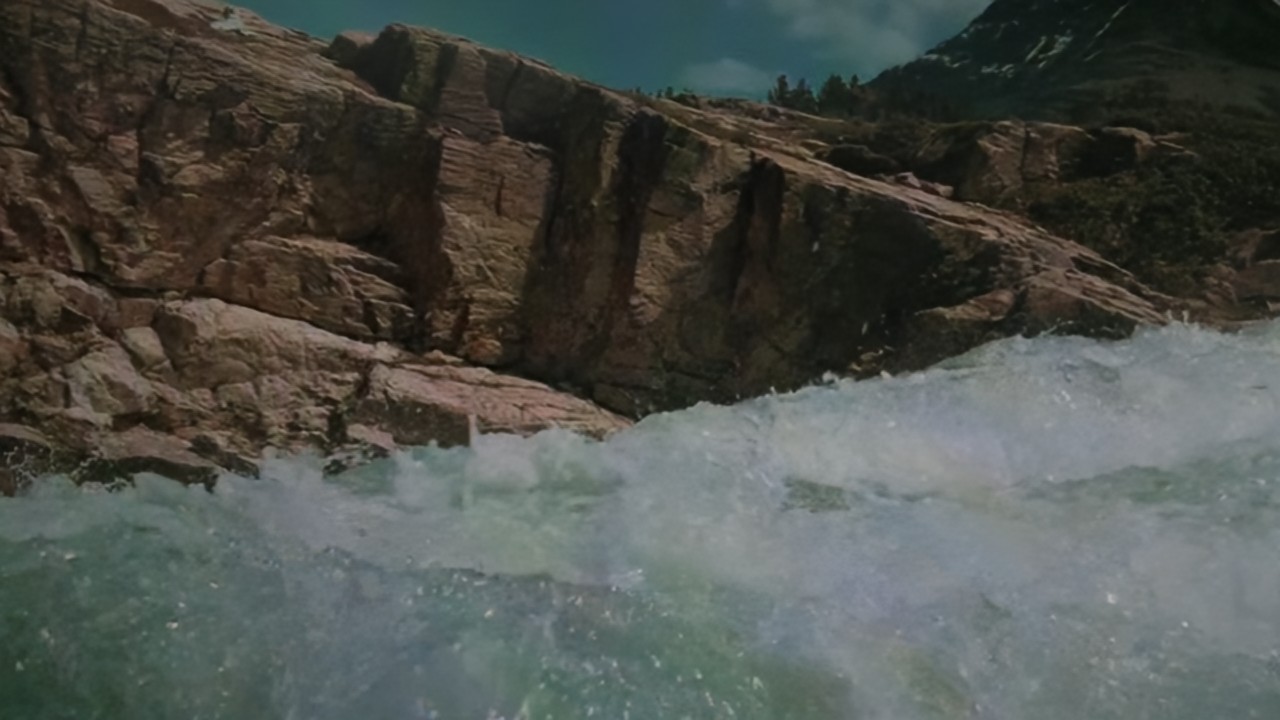



RawVDemoire
Ours
RRID
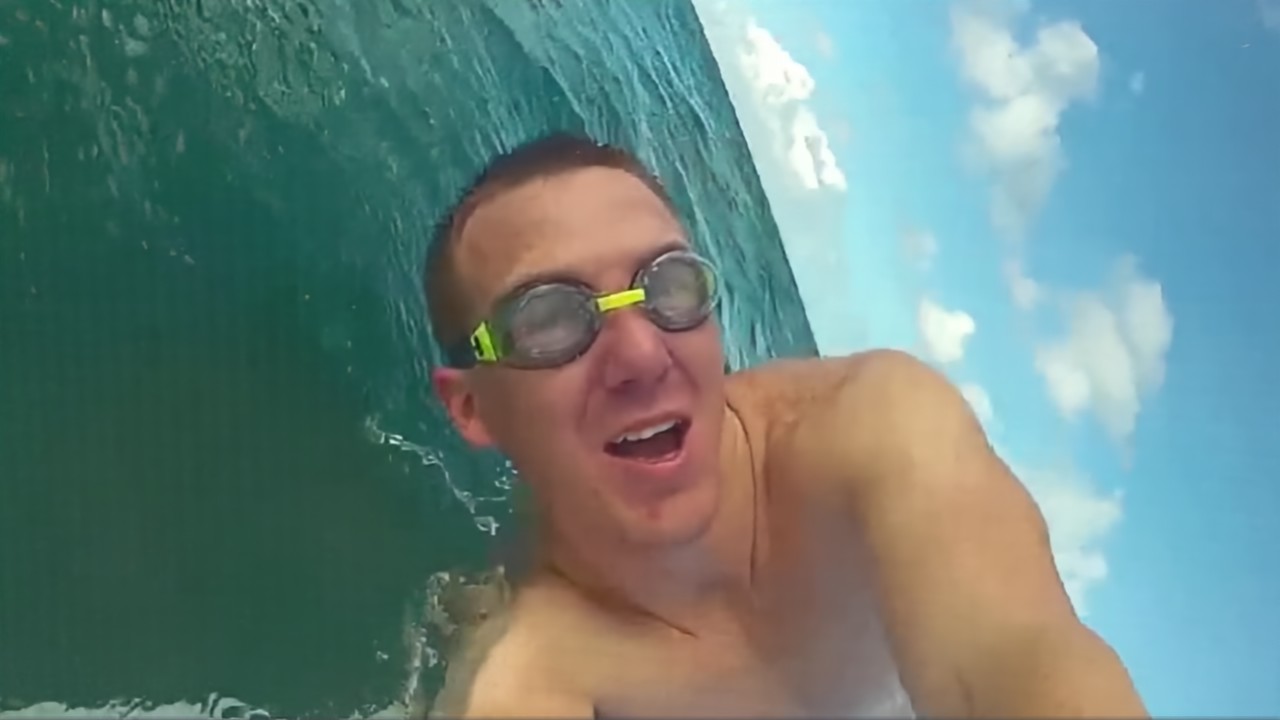



RawVDemoire
Ours
RRID
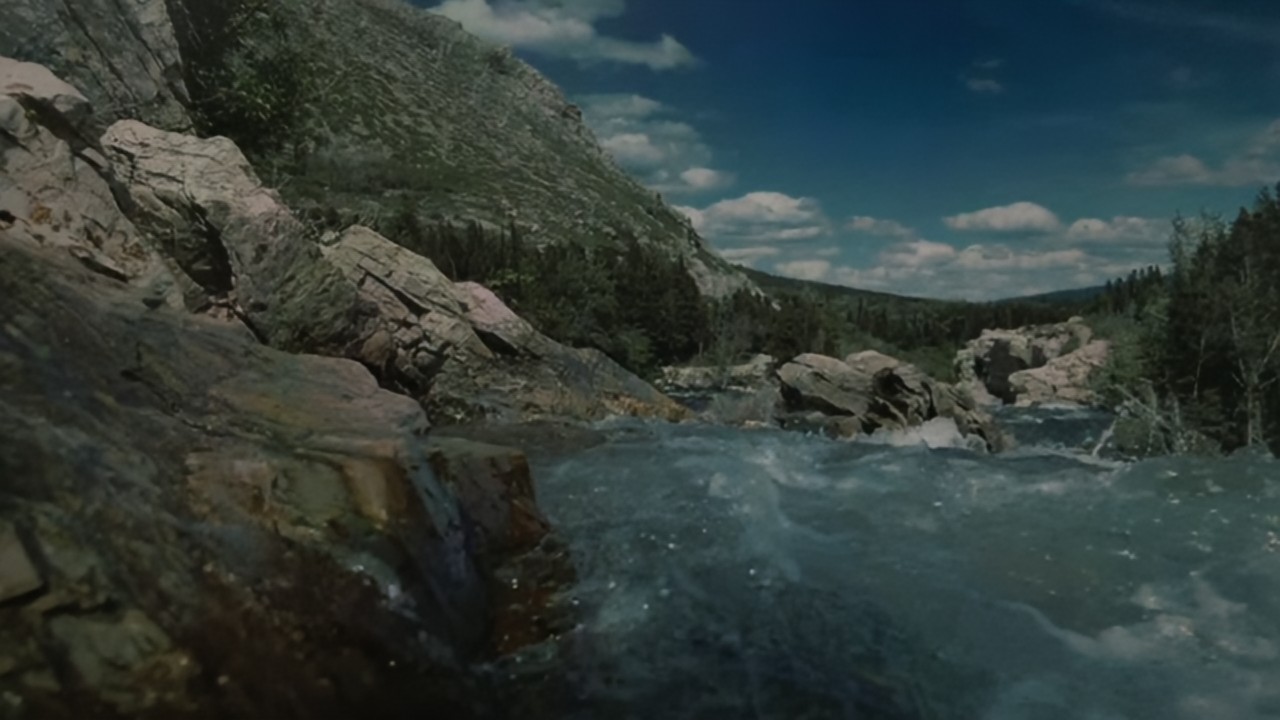
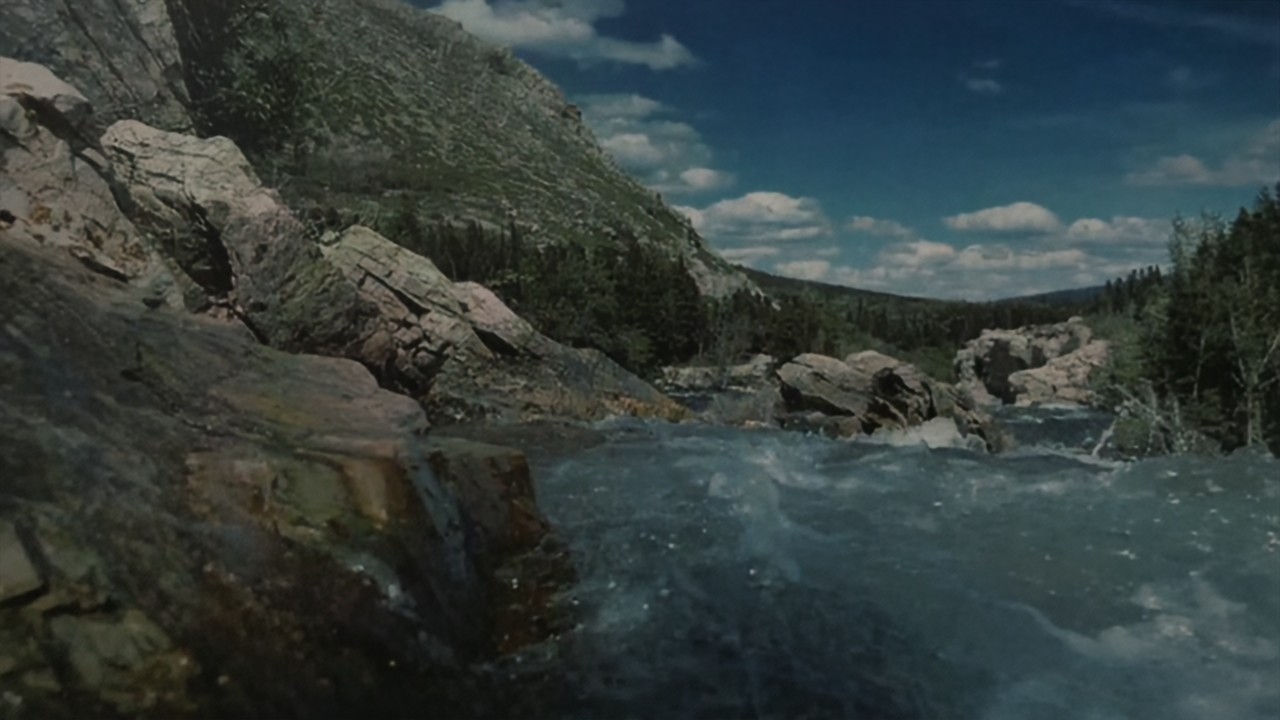
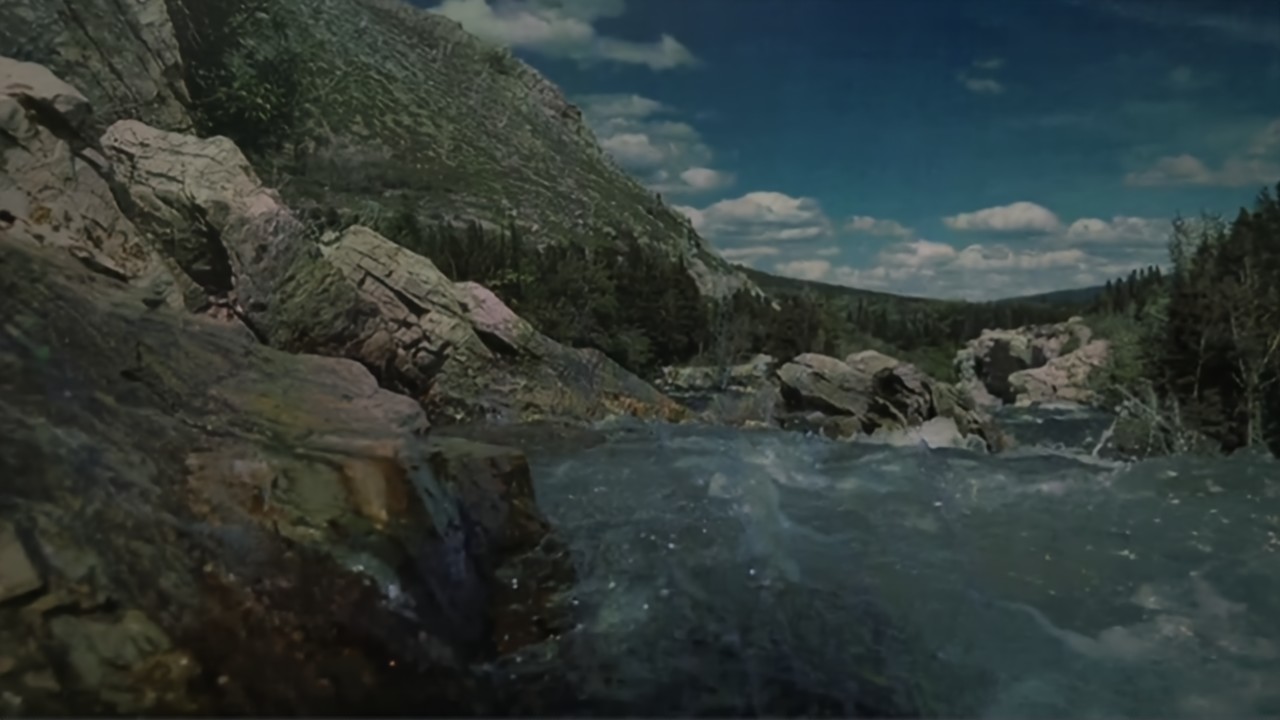



RawVDemoire
Ours
RRID



RawVDemoire
Ours
RRID
RawVDemoire
Ours
RRID